The educational system

Education at different ages
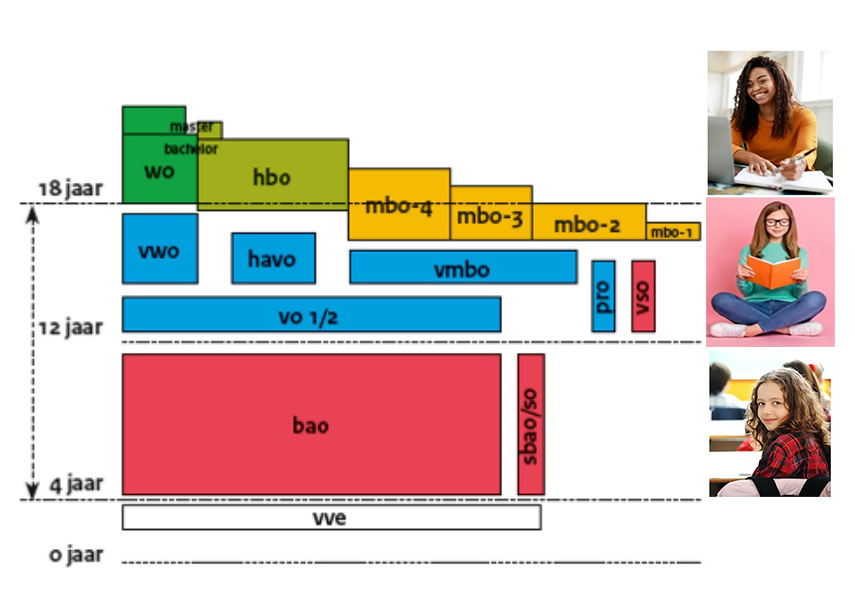
The educational system: overview
Education in the Netherlands is split into several periods:
Daycare and preschool: Kids can go to a daycare (“kleuterdagverblijf”) from age 0 – 4. Next to this we have a variant called preschool. In fact a preschool (“kleuterschool”) resembles daycare but now children go this type of education from age 2 – 4.
Primary school (basisschool): Kids go here from age 4 to 12. They learn to read, write, count, and other subjects which we will discuss in more detail.
Secondary school (voortgezet onderwijs): After primary school children go to secondary education from age 12. There are three types that follow after a first stage of 2 years.
vmbo: This type takes 4 years. It helps children to get ready for middle education (MBO)
havo: This type takes 5 years. It helps kids get ready for higher education (HBO)
vwo: This type takes 6 years. It gets kids ready for university (WO)
VMBO leads to education for having a special job like; carpenter, nurse or mechanic. This type of education is called MBO.
It is a general misconception that higher education always is related to a higher income. A good carpenter can have the same income as a scientific researcher.
Higher education (hoger onderwijs):
There are two types:
Applied science schools (HBO): Here, students learn special skills for jobs.
Universities (WO): Here, students can obtain the highest degrees like bachelor’s or master’s.
School system
Daycare and schools for toddlers
“Kinderdagverblijf”
“Kinderdagverblijf” means child-day-staying. It’s a place for little kids (0 to 4 years old) to play and learn at a safe place when their parents are busy. This “education” is always private. The government in the Netherlands checks to make sure these places are indeed safe and good. As it is private you have to pay for it. Parents that have not the financial means to pay can have financial support from the government. You have to apply for it via the website of the tax office of the Netherlands. You have to use a so called DigiD that can be considered as a digital passport.
In the Netherlands, “kinderdagverblijf” and “kleuteropvang” are both terms related to childcare for young children. However, there are some key differences between the two:
“Kleuteropvang / Kleuterschool/Peuterschool”
“Kleuteropvang / Kleuterschool/Peuterschool” focuses on pre-school activities and preparing for primary school.(literally “toddler care / toddler school”) specifically refers to childcare for children aged 2 to 4 years old. It is often seen as a bridge between “kinderdagverblijf” and primary school. Kleuteropvang typically focuses on pre-school activities and preparing for primary school though literacy, numeracy, and social skills development.

Daycare centre

Education is mandatory
Education in the Netherlands is “verplicht”.
We also speak of “leerplicht” (obligation to learn:
Age 5-16: Full-time education is mandatory for all children between the ages of 5 and 16. This typically starts with primary school (“basisonderwijs”) and follows by secondary education (“voortgezet onderwijs”).
Age 16-18: There’s a “partial leerplicht” for individuals aged 16-18. This means they must still participate in some form of education or training for at least two days per week. This could be secondary education, vocational training (“middelbaar beroepsonderwijs” or MBO), or higher professional education (“hoger beroepsonderwijs” or HBO).
Schools control if children are absent without a reason. If they are absent without a good reason parents will get a fine.
What are the most important subjects in primary school
In primary school, we learn many things. These are the main subjects:
Language: We learn to read, write, and listen.
Math: We learn basic numbers and how to think.
Science: We learn about nature and how things are.
Social studies: We learn about the past, places, and rules.
We also learn:
Arts: We learn music, drawing, and acting.
Physical education: We learn to move and be healthy.
Personal and social: We learn about feelings, friends, and how to be a good person.


How progression is monitored
Teacher Assessments
Teachers continuously assess students’ progress through observations, classwork, and informal tests. This ongoing assessment helps teachers to adapt instruction to meet individual needs and to identify any difficulties during learning.
Portfolios and Reports
Students’ work and progress are often compiled in portfolios or documented in periodic report cards, providing a comprehensive view of their achievements and areas for improvement.
Standardized Tests
In group 8 ij fact the final year of primary education students may take a standardized test, such as the well known CITO-test,This test assesses the level in core subjects like Dutch, mathematics, and study skills. The results help to give recommendations for the next stage (next type of school).
Freedom of education
In the Netherlands, everyone can choose the school they like for their kids. You can pick a public school, a private school, or one with religious ideas.
The government gives money to all these schools if they are good. So, parents have many choices for their kids’ school.
Schools can also choose what they teach and how they teach. This is good because schools can do what’s best for their students.
What’s good about this?
Parents can choose the best school for their kids.
Schools can teach in different ways.
Schools can try new ways of teaching.
Schools must do a good job because parents are watching.
But, there are also some problems. The government checks to make sure all schools are good. And, they help families who don’t have a lot of money so their kids can go to a good school.
In the end, this freedom in schools is good in the Netherlands. It helps kids get the best education.

Freedom