
War
World War II
Nazi Germany
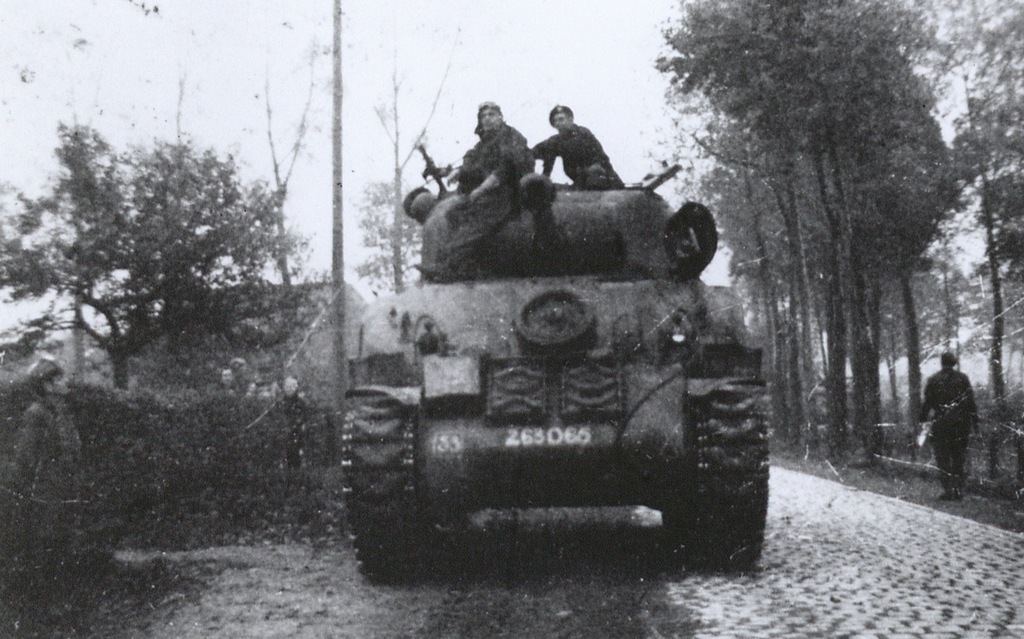
During World War II, the Netherlands was taken over by Nazi Germany, led by Adolf Hitler. German troops invaded the country in 1940, and after a short fight, the Dutch surrendered. The occupation lasted until 1945, and it was a difficult time for the Dutch people. The city of Rotterdam was destroyed by bombings. The Dutch stopped fighting, and the queen fled to England.
Situation of the Jews
Hitler blamed Jewish people for Europe’s problems. Jews had their rights limited, were put in prisons, and sent to camps. In these camps, many were killed in gas chambers or died from illness and starvation. Some Jews hid in secret places, known as people in hiding. Six million Jews were killed in total.
Finally freedom
The war brought hardship, with little food and cold weather. Anyone helping Jews was punished. Hitler also tried to conquer Russia, but the harsh winter conditions made it difficult for German soldiers. Countries like America, Canada, England, and Russia fought against Germany. In 1945, Germany was defeated, and on May 5th, the Netherlands was liberated.
Anne Frank
Anne Frank was a Jewish girl who lived in Amsterdam during World War II. She and her family went into hiding in 1942 to avoid being captured by the Nazis, who were rounding up Jews and sending them to concentration camps. Anne and her family lived in a secret annex for two years before they were betrayed and captured by the Nazis in 1944. Anne died in a concentration camp in Germany in 1945, at the age of 15.
Her famous diary
Her diary, which she kept while in hiding, was later published and has become one of the most widely read books in the world, providing a personal and poignant account of the atrocities of the Holocaust.
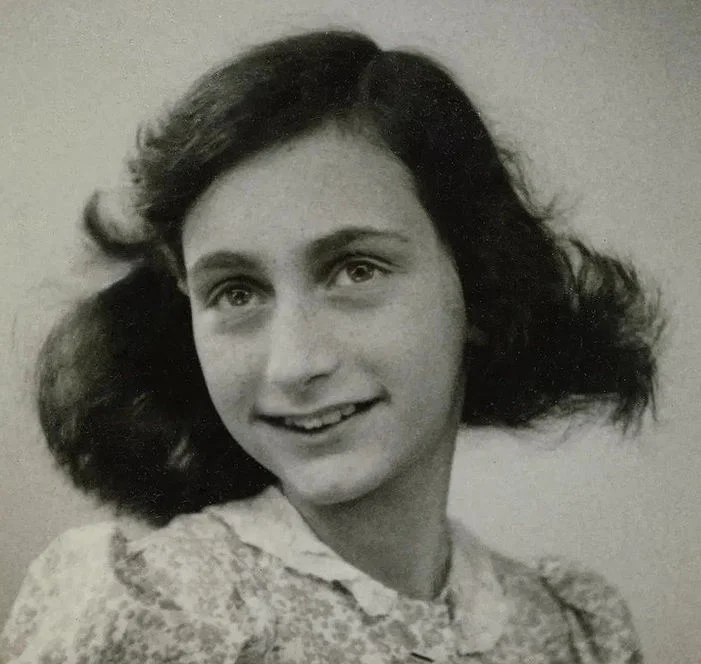
Anne Frank

Flood disaster 1953
After the end of the war
After the end of World War II in 1945, the Netherlands underwent a period of rebuilding and reconstruction. The country had suffered greatly during the war, with large parts of its infrastructure destroyed, and many of its citizens killed or displaced. However, the Dutch people were determined to rebuild, and with the help of foreign aid and government programs, the country was able to recover.
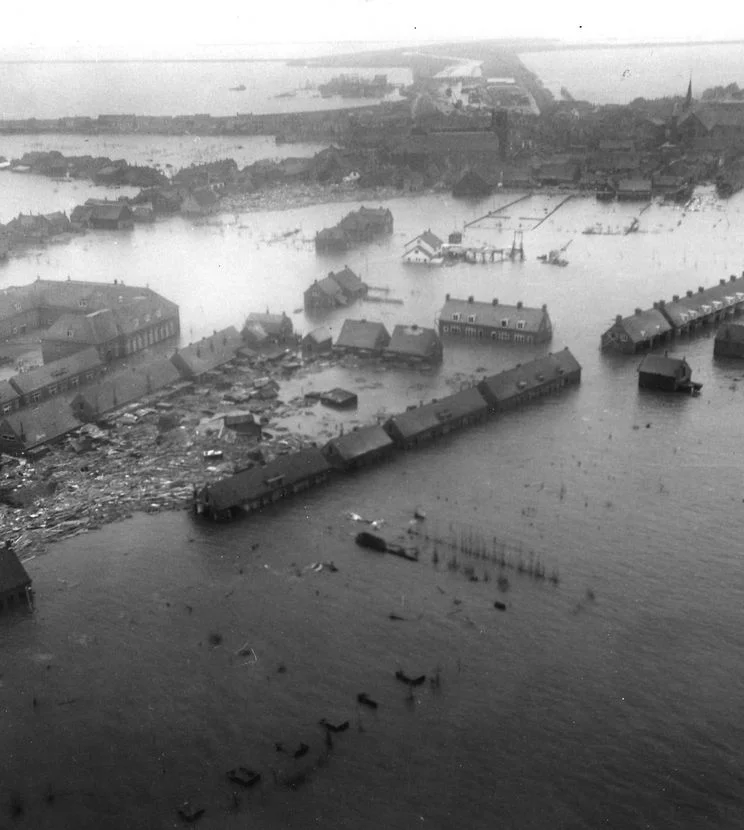
The post-war period saw significant social, economic, and political changes in the Netherlands. The country became more prosperous and developed, with a strong focus on social welfare and the creation of a modern welfare state. In 1953 there was a disaster. A large part of the country, especially the province of Zeeland, was flooded. More then 1800 people died. After this, the dikes were reinforced and new dams were made (the project was called Delta-plan).
Joining United Nations
he Dutch also played an active role in the international community, joining the United Nations and other international organizations.
In the decades that followed, the Netherlands became known for its liberal and tolerant attitudes towards social issues, such as drug policy, euthanasia, and same-sex marriage.
Joining NATO
The Netherlands is a member of NATO. When a country joins NATO, it means they become a member of a group called the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. NATO is made up of countries from North America and Europe. The main goal of NATO is to work together to defend and protect each other. Therefore it is a military organization.
People from other countries
1970, new immigrants
Around 1970 the economy grew strongly. The Dutch did not want to do a lot of work that had to be done. People were brought from Turkey and Morocco who were willing to do this work. These immigrants are called “guest workers”. Many went back but many also stayed. This led to important shifts in the composition of the population, especially in large cities such as Rotterdam and The Hague. That resulted in tensions. Nowadays it is difficult to enter the Netherlands. The Civic Integration Act has been in force since 2007.
People from the European Union
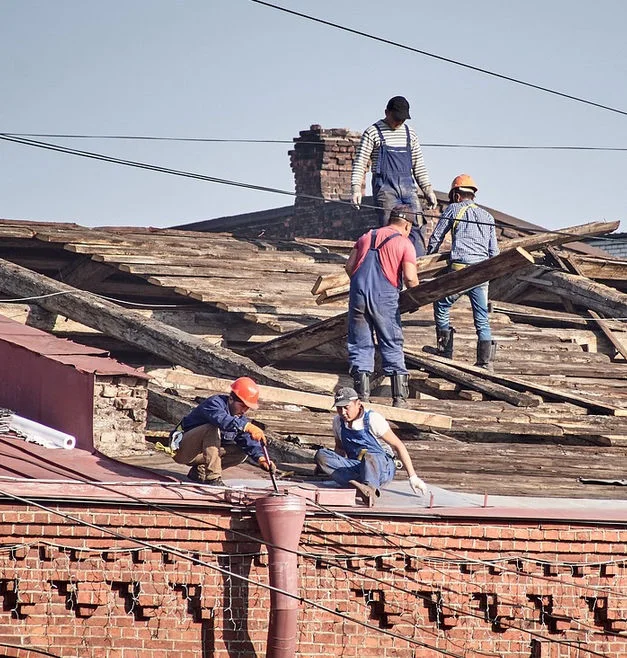
As people form the European Union are free to travel, many people of for instance Polen and Romania entered the country. For example, many people from Poland work in construction.

Guest Workers, many came from Polen